Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Welcome to our comprehensive guide to solar rapid shutdown. In this article, we will delve into the important topic of rapid shutdown in solar arrays and its significance for fire safety. We will explore the requirements set by the National Electrical Code (NEC) and how rapid shutdown works to protect both first responders and solar system owners.
It is a critical safety feature that allows for the quick de-energizing of a rooftop solar panel system in case of an emergency. It ensures that utility line workers and firefighters are protected from potential electrical hazards when working on or around the solar array. Without it, even if the inverter is turned off, solar panels can still generate power and pose a risk to those handling the system.
Throughout this guide, we will discuss the different types of solar inverters and how they comply with requirements. We will also explore the adoption of regulations by states and the variations in requirements across the country.
Whether you are a solar system owner, installer, or simply interested in understanding the importance of rapid shutdown solar, this guide will provide you with the necessary information to navigate the world of solar safety regulations. So let’s dive in and explore the world of solar rapid shutdown!
What is Rapid Shutdown in a Solar Array?
It is a crucial safety feature for rooftop solar arrays. It involves quickly de-energizing a solar energy system to protect utility line workers and first responders during emergencies or power outages. Without shutdown, solar panels can continue to send high-voltage power into the grid, posing a risk of injury to those working to restore power or address emergency situations.
It consists of two components: a piece of equipment within the solar array and compliance with the National Electrical Code (NEC). The equipment, such as a rapid disconnect switch, is designed to shut off the flow of electricity from the solar panels to the grid in less than 60 seconds. This feature ensures the safety of utility workers and first responders by minimizing the risk of electrical shock.
The NEC, a set of electrical safety standards, includes requirements to protect firefighters and other emergency personnel. These requirements have evolved over time, with the most recent versions being NEC 2017 and NEC 2020. The specifics of rapid shutdown vary depending on the NEC version adopted by each state.
The implementation of solar rapid shutdown depends on the type of solar inverter used in the system. String inverters may require additional module-level power electronics (MLPE) to achieve shutdown compliance, while microinverters are inherently rapid shutdown-capable. Installers may use different types of firefighter solutions based on location, customer preferences, and other factors.
While shutdown is not a federal law, many states have adopted the NEC guidelines as part of their electrical code. It is important for homeowners to familiarize themselves with the requirements in their state or municipality to ensure compliance and prioritize the safety of their solar panel systems.
The Importance of Solar Rapid Shutdown for Fire Safety
Ensuring fire safety is a top priority when it comes to solar panel systems. It plays a crucial role in protecting both homeowners and first responders in case of an emergency.
During a power outage, a solar energy system can continue to send high-voltage power into the grid, posing a significant risk to utility line workers who are trying to restore power. It allows for the quick de-energizing of a photovoltaic (PV) system, reducing the risk of injury to these workers.
The National Electrical Code (NEC) in the United States has recognized the importance of solar rapid shutdown and has made it a requirement for solar installations. By implementing guidelines, firefighters and other first responders can safely handle solar panel systems during emergency situations.
Rapid shutdown works by reducing the power output of a solar system to a safe level within 60 seconds or less. This can be triggered by a physical shutdown initiation switch on the system, which allows firefighters to quickly and effectively deenergize the system.
Different types of solar inverters have different approaches to shutdown. String inverters, for example, may require the installation of module-level power electronics (MLPE) to enable fast shutdown. On the other hand, microinverters have built-in module-level shutdown functions, eliminating the need for additional devices.
While it is not a federal law, many states have adopted the NEC guidelines and made fast shutdown a requirement. It is important for homeowners to be aware of the requirements in their state or municipality to ensure compliance and enhance the safety of their solar panel systems.
By understanding the importance of fast shutdown for fire safety, homeowners can make informed decisions about their solar installations and work closely with installers to ensure compliance with the necessary guidelines.
Understanding the National Electrical Code (NEC)
The National Electrical Code (NEC) plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and compliance of electrical installations, including solar energy systems. As solar power continues to gain popularity, it is important for homeowners and installers to understand the NEC requirements for rapid shutdown.
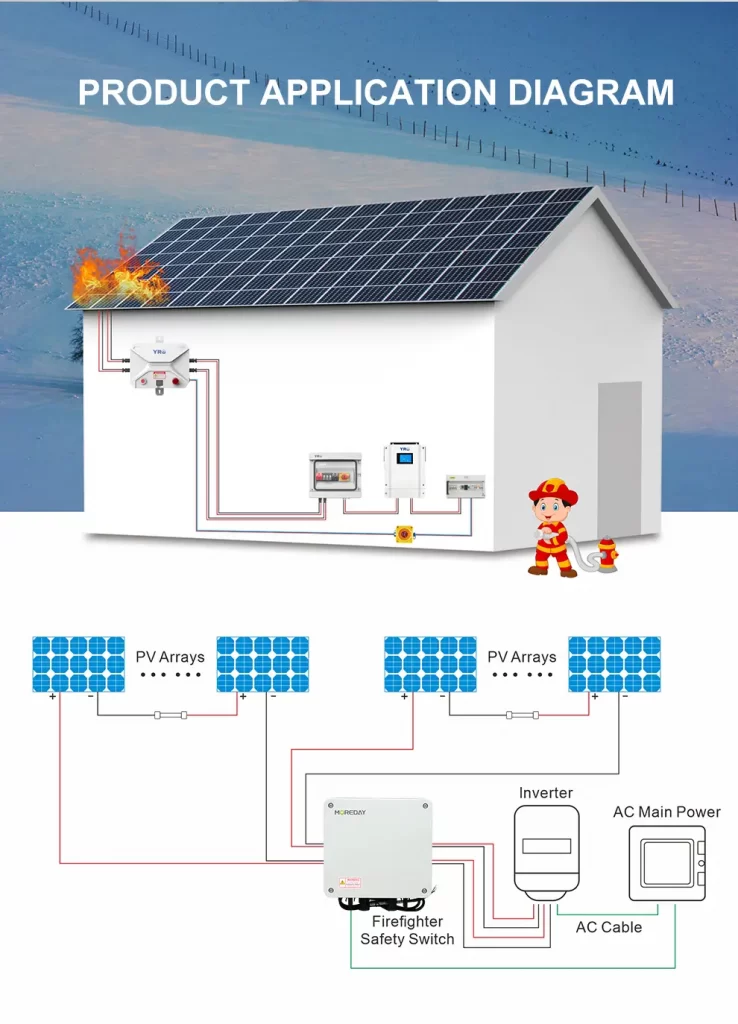
The NEC is a set of standards and guidelines established by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA). It provides regulations for the installation and operation of electrical systems, including solar panels. The NEC is not a federal law, but rather a code that is adopted and enforced by individual states.
Fast shutdown is a requirement outlined in the NEC to enhance the safety of solar energy systems during emergency situations. It involves quickly de-energizing the system to protect utility line workers and first responders from potential electrical hazards. By implementing fast shutdown, solar arrays can be safely shut off during power outages or emergencies.
The specific requirements depend on the version of the NEC being enforced in a particular state. The NEC 2014 and NEC 2017 editions have different criteria for rapid shutdown, including the location of the shutdown initiation device and the voltage levels that must be achieved within a certain timeframe.
To ensure compliance with NEC requirements, it is essential to work with a reputable and experienced solar installer who is knowledgeable about the specific regulations in your state. They can help design and install a system that meets all the necessary guidelines.
By understanding and adhering to the NEC regulations, homeowners can ensure the safety of their solar energy systems and provide peace of mind for themselves and first responders.
How Does Rapid Shutdown Work?
It is an essential safety feature for solar panel systems, designed to quickly de-energize the system in case of an emergency. But how does it actually work?

When a rapid shutdown is initiated, the goal is to reduce the power output of the solar system to a safe level within 60 seconds or less. This is crucial to protect firefighters and other first responders who may need to access the area around the solar panels during an emergency.
The specific method of rapid shutdown depends on the type of solar inverter used in the system. For systems with string inverters, the panels continue to produce electricity as long as the sun is shining. In this case, a physical shutdown initiation switch is installed on the system, which can be triggered by firefighters to cut off the power.
If the system includes power optimizers or microinverters, rapid shutdown is inherent in their design. These devices have built-in module-level rapid shutdown functions, which means that the power output of each individual panel can be quickly reduced to a safe level. This eliminates the need for additional rapid shutdown devices.
It’s important to note that rapid shutdown is not a federal law, but rather a requirement set by the National Electrical Code (NEC) and adopted by individual states. The NEC has refined the guidelines for rapid shutdown in recent years, making it a standard safety measure for solar panel systems.
To ensure compliance with rapid shutdown requirements, it’s recommended to work with a qualified solar installer who is familiar with the NEC guidelines. They can help determine the best approach for your specific system and ensure that all necessary components are in place for rapid shutdown functionality.
By prioritizing rapid shutdown in your solar panel system, you can enhance the safety of your home and protect first responders in the event of an emergency.
Types of Solar Inverters and Rapid Shutdown
When it comes to rapid shutdown for solar systems, the type of solar inverter used plays a crucial role. There are two main types of solar inverters: string inverters and microinverters.
String inverters are the traditional choice for solar installations. They are connected to multiple solar panels in a series, forming a string. However, when it comes to rapid shutdown compliance, additional components may be required. In some cases, string inverters can incorporate power optimizers or module-level power electronics (MLPE) to enable rapid shutdown capabilities. This allows for the reduction of power output to a safe level in the event of an emergency.
On the other hand, microinverters are inherently rapid shutdown-capable. They are installed on each individual solar panel, allowing for module-level control and monitoring. With microinverters, there is no need for additional rapid shutdown devices or MLPEs to comply with NEC guidelines.
It’s important to note that the choice between string inverters and microinverters may vary depending on factors such as location, customer goals, and installer preferences. Some installers may favor one type over the other, while others may offer both options.
When considering a solar panel system, it’s crucial to discuss with your installer which type of inverter is being used and whether it meets the rapid shutdown requirements in your state or municipality. This will ensure that your solar system is not only efficient but also compliant with safety regulations.
State Adoption of Rapid Shutdown Requirements
State adoption of rapid shutdown requirements for solar systems varies across the United States. The National Electrical Code (NEC) sets the standards for electrical safety, including regulations. While the NEC is not federally mandated, individual states can choose to adopt and enforce the code.
As of 2023, many states have adopted NEC 2017 or NEC 2020, which require it at the module level.Solar systems must comply with rapid shutdown requirements to pass inspections and be connected to the utility grid.
However, some states have not adopted the NEC rapid shutdown guidelines. These states include Arizona, Illinois, Mississippi, and Missouri. Although these states have not implemented statewide requirements, certain municipalities within these states may choose to enforce the NEC guidelines.
It’s essential for homeowners to be aware of the rapid shutdown requirements in their state or municipality. This knowledge can help when discussing system design with installers and ensure compliance with local regulations. Additionally, homeowners with existing solar systems should stay informed about the requirements to update their systems for safety or future expansions.
To ensure compliance with rapid shutdown requirements, it is recommended to consult with qualified solar installers who are familiar with the specific regulations in your area. They can guide you through the process of choosing the right equipment and ensuring your solar system meets all necessary requirements.
By staying informed and working with knowledgeable professionals, homeowners can ensure the safety and compliance of their solar panel systems with rapid shutdown regulations in their state.
Derek Ke
Hey, I’m Derek Ke, the founder of Moredaydc.com, an expert in solar electrical products and ev charging.
In the past 15 years, we have helped 60 countries and nearly 500 customers (such as farms, residences, industrial and commercial) solve new energy and green power problems. This article aims to share more knowledge about solar electricity and new energy with everyone, so that green electricity can enter every home.
Common Queries
Frequently Asked Questions
please feel free to contact us.
A: The primary purpose is to quickly reduce the voltage in solar panels and associated electrical circuits to a safe level during emergencies, such as fires, thereby minimizing the risk of electrical shocks and enhancing safety for emergency responders and maintenance personnel.
A: It is designed to deactivate a solar array very quickly, typically reducing the voltage to a safe level within seconds. Specific timeframes can vary based on the system design and regulatory requirements.
A: The requirement varies depending on local regulations and building codes. In many regions, such as the United States, these systems are mandated by the National Electrical Code (NEC) for new solar installations.
A: Yes, can often be retrofitted to older solar panel systems. The feasibility and specifics of retrofitting depend on the existing solar panel model and configuration.
A: Solar rapid shutdown devices have minimal impact on the overall power output of solar panels. While they require additional components, modern systems are designed to ensure that any loss in efficiency is negligible.
A: Yes, there are different types available, varying in terms of technology, integration method, and compatibility with different types of solar installations.
A: Maintenance requirements for solar rapid shutdown devices include regular inspections and testing to ensure they are functioning correctly. The specific maintenance schedule can vary based on the manufacturer’s recommendations and environmental factors.
A: It enhance safety by quickly reducing the voltage in the solar panels to a safe level during emergencies, preventing electric shocks and allowing safe access for emergency responders and maintenance crews.
A: Yes, can be integrated with smart home technology, allowing for remote monitoring and control, and enhancing the overall management and safety of the solar installation.
Make Electricity Available To All People






