MOREDAY currently supports OCPP 1.6 in production environments and is actively developing firmware and platform support for OCPP 2.0/2.0.1. This article provides an objective overview of OCPP and cites community/industry resources where appropriate.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is OCPP?
OCPP (Open Charge Point Protocol) is an open, vendor-neutral protocol that defines how EV charging stations (charge points) communicate with a central system (the backend / Central System Management Software — CSMS). Its purpose is simple: interoperability. Instead of each charger vendor inventing a proprietary remote control or data format, OCPP provides a standard message set and behavior so charging hardware and management platforms can interoperate.
Why “open” matters:
- Operators can change backend providers without replacing all chargers.
- Manufacturers can implement a common interface so customers aren’t locked into a single software stack.
- The ecosystem evolves faster when specifications are public and collaboratively improved.
The Open Charge Alliance (OCA) stewards OCPP and publishes the protocol specifications and reference resources.
A short history and the common versions you will see
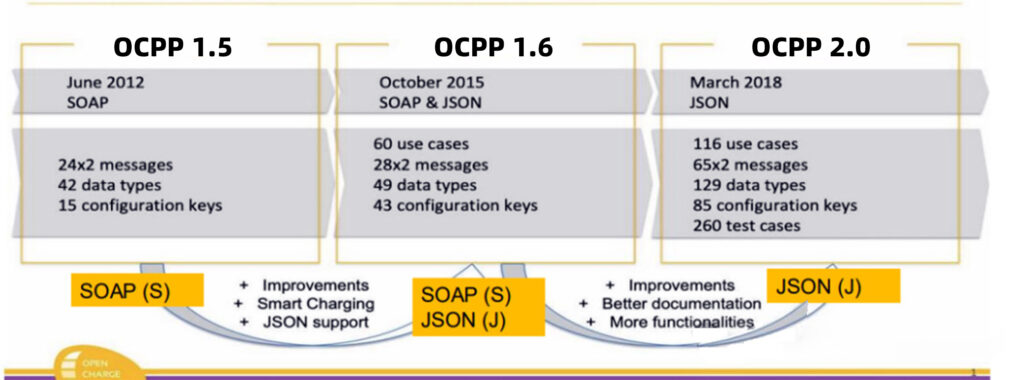
Key versions in practical use:
- OCPP 1.2 / 1.5 — early releases that introduced the basic idea.
- OCPP 1.6 — the most widely deployed version; supports JSON over WebSocket, smart-charging basics, remote diagnostics, and session management (MeterValues, Start/StopTransaction, etc.). Many installed chargers and networks still rely on 1.6 today.
- OCPP 2.0 → 2.0.1 — major evolution adding richer device management, improved smart-charging features, native security profiles, better transaction handling, ISO 15118 integration (Plug & Charge), richer diagnostics, and messaging/display capabilities. 2.0.1 is the stabilized update used by many forward-looking projects.
- Important compatibility note: OCPP 1.6 and OCPP 2.0/2.0.1 are not backward-compatible; many sites run a hybrid mix and rely on backends capable of handling both protocols.
How OCPP actually works *technical overview without getting lost*
OCPP is a message-based protocol between two logical endpoints:
- Charge Point (CP) — the charger hardware (embedded controller + network).
- Central System (CSMS) — the backend server that manages the CPs.
Transport and formats
- OCPP 1.6: commonly uses JSON over WebSocket (though SOAP was earlier supported).
- OCPP 2.0/2.0.1: also uses WebSocket/JSON and adds formalized profiles and enhanced payloads.
Typical message flow (simplified)
- BootNotification — Charger boots and identifies itself to the central system.
- Authorize / StartTransaction — User authentication and start of a charging session.
- MeterValues — Periodic meter reads for billing and monitoring.
- StatusNotification — Charger reports state (available, preparing, charging, fault).
- Remote command — Central system sends RemoteStartTransaction, FirmwareUpdate, or configuration commands.
The protocol defines both the message names and the expected payloads so both sides have an agreed behavior. This makes development and debugging much easier compared with ad-hoc APIs.
OCPP versions compared: 1.6 vs 2.0.1 *what changes for operators and manufacturers*
Here are the practical, decision-relevant differences:
OCPP 1.6 (why it’s still dominant)
- Stable, widely supported by hardware vendors.
- Provides the core session handling and basic smart-charging (profiles).
- Simple to implement on resource-constrained devices.
- Often requires external security (VPN/TLS setups) to meet high security needs.
OCPP 2.0/2.0.1 (why projects choose it now)
- Native support for device management (configuration, monitoring) — valuable for fleets and large deployments.
- Advanced smart charging features and better integration with ISO 15118 (Plug & Charge).
- Enhanced security model, including certificate-based authentication and stronger encryption patterns.
- More expressive message sets: UI/display control, diagnostics, reservation extensions, firmware management improvements.
Practical takeaways
- For brownfield sites with large installed base: continue with OCPP 1.6 and plan gradual upgrades.
- For greenfield projects targeting advanced features (Plug & Charge, V2G, sophisticated load control): spec OCPP 2.0.1 or 2.1 where available, and ensure hardware/backends support it.
Most modern commercial EV chargers — including MOREDAY’s DC fast chargers — support OCPP 1.6 or OCPP 2.0.1, ensuring seamless connection with multiple network operators and platforms.
OCPP software *what the backend does and why it matters*
When people search “OCPP software” they are usually looking for the backend systems that implement the Central System features. The backend (CSMS) is the operational heart of a charging network and typically provides:
- Real-time monitoring and dashboards (status, faults, utilization).
- User and session management (authentication, RFID, apps, billing).
- Billing and payment integration.
- Smart charging algorithms (dynamic load balancing, time-of-use optimization).
- Maintenance tools (remote diagnostics, logs, firmware updates).
Some vendors provide cloud SaaS CSMS; others offer on-premise solutions. A robust OCPP software must handle message queuing, retries, security, and device diversity. MOREDAY integrates with leading CSMS platforms and offers our own manager for operators who want tight operational control.

Security: common myths and the real picture
Security became a major focus with OCPP 2.0. Key points:
- OCPP 1.6 can be made secure using TLS/VPN and good operational practices, but many installations used insecure approaches historically.
- OCPP 2.0.1 introduces more built-in security features (certificate management, improved authentication flows). This reduces reliance on out-of-band solutions and simplifies secure deployments.
Operators should expect:
- Mutual authentication between charger and central system (certificates).
- Encrypted transport with strong cipher suites.
- Regular firmware updates and secure key management as part of lifecycle operations.
Is Tesla Wall Connector OCPP? *concise, evidence-based answer*
Short answer: Most Tesla Wall Connectors (Gen 3 and consumer-grade units) are not generally OCPP-controllable by third-party backends. Tesla’s consumer wall chargers historically communicated through the Tesla cloud and app, not open OCPP backends. Various community reports and charger management vendors confirm that third-party OCPP integration with Tesla home chargers is limited or unavailable at the time of many reports.
That said, the market is evolving. There are persistent reports and announcements suggesting Tesla may add broader OCPP support for certain products or enterprise solutions over time; these announcements should be checked against Tesla’s official releases before assuming compatibility. In short: don’t assume Tesla home chargers are OCPP-compatible unless explicitly documented by Tesla.

Implementation realities and constraints
When implementing OCPP in real projects you must consider:
- Hardware capabilities — older controllers may lack memory/CPU for full 2.0 features. There are minimal-footprint strategies but tradeoffs exist.
- Protocol co-existence — many operators run mixed fleets (1.6 and 2.0). Ensure your CSMS supports both.
- Security lifecycle — plan certificate rotation, firmware channels, and incident monitoring.
- Testing and conformance — use OCA test suites and interoperability events; don’t rely only on unit tests.
- Feature mapping — map required features (Plug & Charge, reservations, V2G) to OCPP version capabilities before procurement.
MOREDAY’s stance and practical roadmap
- Today (production): MOREDAY supports OCPP 1.6 across our DC and AC product lines to maximize compatibility with the broad installed base of CSMS platforms. This enables operators to deploy with confidence and integrate into most existing networks.
- Roadmap (in development): We are actively developing and testing OCPP 2.0/2.0.1 capabilities (device management, advanced security, ISO 15118 integration) to provide customers with future-proof chargers that support Plug & Charge, stronger security, and richer diagnostics. Our approach is staged: enable 2.0 on capable hardware while ensuring graceful interoperability with 1.6 systems where operators need it.
Practical recommendations *for operators, integrators, and buyers*
- If you manage an existing network: Keep using OCPP 1.6 for stability; plan phased upgrades. Use CSMS providers that can orchestrate both 1.6 and 2.x devices.
- If you’re procuring new chargers: Prefer chargers that declare OCPP 2.0.1 readiness if your project expects Plug & Charge, advanced load management, or long lifetimes. Ensure the vendor provides firmware and security lifecycle support.
- If you want home chargers controlled by third-party software: Verify vendor compatibility explicitly. Don’t assume all consumer chargers (including many Tesla Wall Connectors) will interoperate with OCPP systems.
Looking forward: OCPP and the electrified grid
OCPP is evolving alongside the grid — the protocol is the enabler for intelligent behaviors such as:
- Smart charging coordinated with grid signals and tariffs.
- Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) or vehicle-to-home (V2H) implementations (requires additional standards & hardware).
- Plug & Charge (ISO 15118) for seamless authentication and payment.
- Energy-storage + charger coordination to optimize renewable energy usage.
For planners, OCPP 2.0.1 is the switching point where these advanced integrations become practical at scale.

Closing
- OCPP is the open, community-driven protocol that makes EV chargers and backends interoperable.
- OCPP 1.6 is the currently dominant, proven standard; OCPP 2.0.1 brings important new features (security, device mgmt, ISO 15118 support) and is the future direction.
- Tesla Wall Connectors are not generally OCPP-controllable by third-party backends — verify vendor documentation for specific claims.
- OCPP software (CSMS) is essential: it provides monitoring, billing, smart charging, and remote management. Choose a backend that supports the OCPP versions you need.
- MOREDAY: supports OCPP 1.6 now; actively developing 2.0/2.0.1 support for future capabilities.
Ryan Huang
Hello everyone, I’m Ryan Huang, founder of Moreday, a company specializing in solar-powered ev charging solutions and pv power transmission and distribution. Over the past 17 years, we’ve helped nearly 6000 customers in 67 countries (including farms, residential, industrial, and commercial users) solve their renewable energy and green power needs. This article aims to share more knowledge about renewable energy and solar power, bringing sustainable electricity to every household.


