J1772 is not considered a “fast charger” because it does not support DC (direct current) fast charging. J1772 is an AC charging interface standard widely used in electric vehicles.
J1772 is mainly used for Level 1 and Level 2 charging, that is, charging with 120V or 240V AC power supply, which means that its charging speed is relatively slow and is usually used in home or public AC charging piles. In this article, we will learn about J1772 chargers and some basic differences between them and fast chargers.
What Is a J1772 Connector?
J1772, also known as SAE J1772, is a standardized charging connector widely used in electric vehicles in the United States and Canada. The J1772 standard was developed by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) and is a Level 1 and Level 2 charging standard, primarily for AC charging.
J1772 connectors are commonly used in public charging stations, home wall chargers, and portable electric vehicle chargers. Designed for compatibility, it can charge nearly all modern electric vehicles in North America, making it a convenient option for many drivers.
1. Main Advantages of the J1772 Connector
Although J1772 is not a fast charger, it also has many advantages for users who love to use J1772 chargers:
- Strong compatibility: widely applicable to most electric vehicles in North America and Japan, convenient for use in more public charging stations.
- Safe and reliable: multi-layer protection design to avoid short circuits and electric shock, ensuring safe use.
- Durable design: sturdy structure, waterproof and dustproof, suitable for frequent plugging and unplugging.
- Flexible charging: supports 120V and 240V charging needs to meet different scenarios.
- Wide infrastructure: public charging stations are generally equipped with J1772 interfaces, which are convenient for daily and long-distance charging.
2. Limitations of J1772 and How to Overcome Them
The main limitation of the J1772 connector is that it cannot provide DC fast charging, which means it is not well suited for fast charging on long trips. Here are some tips to overcome this limitation:
- Plan a trip with DC fast charging stations: For long trips, plan your route around charging stations that offer DC fast charging options. Apps like PlugShare and ChargePoint can help you find these charging stations.
- Use multiple charging methods: Many EV owners use a J1772 Level 2 charger at home and a DC fast charger when on the road. This combination provides the flexibility of charging overnight at home and fast charging while on the road.
Technical Design of the 1772 Connector
The J1772 connector uses a standardized five-pin design that includes:
- AC Line 1 and Line 2: These two wires carry AC power.
- Ground Pin: Provides grounding for safety.
- Proximity Detection: This is a sensor pin that detects when the connector is plugged in and allows for safe connection and disconnection.
- Control Pilot: A pin is used for communication between the vehicle and the charger to ensure the correct power level.
J1772 chargers are typically rated between 3.3 kW and 19.2 kW. However, even at the higher end of the Level 2 power range, J1772 still does not achieve the charging speeds required for traditional fast charging.
Differences Between Level 1, 2, and Level 3 Chargers
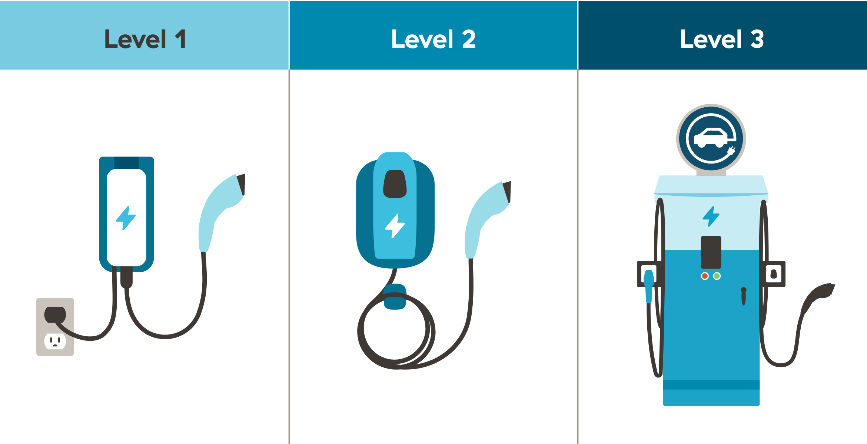
To understand why J1772 is not a fast charger, let’s look at the differences between Level 1, 2, and 3 charging:
1. Level 1 Charging
This is the slowest type of EV charging and is typically charged via a regular 120-volt household outlet. Using the J1772 connector, Level 1 charging adds about 2 to 5 miles of range per hour and is suitable for overnight charging or when the EV is not immediately in use.
It is a practical solution for those with a shorter daily commute or a home charging setup that does not require a large installation.
2. Level 2 Charging
J1772 is often associated with Level 2 charging, which uses a 240-volt power source, similar to what a typical electric dryer uses. Level 2 charging is faster than Level 1, typically providing 10 to 60 miles per hour.
For most EV owners, Level 2 charging offers the best balance between convenience and speed, making it a popular choice for both home and public chargers.
However, while Level 2 charging is faster than Level 1, it is not considered “fast charging” because the high-speed charging provided by DC charging stations is the definition of this type of charging.
3. Level 3 (DC Fast Charging)
To be classified as a fast charger, the charger must typically provide direct current (DC) fast charging, which can significantly reduce charging time.
These chargers are designed for high-speed charging, typically providing 50 to 350 kW of power, and can charge an EV battery to 80% in just 20 to 40 minutes. Importantly, the J1772 standard does not support DC charging and therefore does not qualify as a fast charger.
Differences Between J1772 and DC Fast Charging Standards
The main differences between J1772 and DC fast chargers such as CCS (Combined Charging System) and CHAdeMO are the current type and charging speed.
- J1772: As an AC charging standard, J1772 is limited to Level 1 and Level 2 charging speeds, suitable for overnight charging or locations where the vehicle is parked for long periods of time. It is reliable, but not suitable for fast charging.
- DC Fast Charging (CCS and CHAdeMO): These connectors use DC power for faster charging, charging the EV battery directly without the need for an onboard AC-DC converter. Fast charging stations are often located along highways and are ideal for EV drivers who need to charge quickly on long journeys.
Where and When to Use J1772 Chargers

While J1772 chargers are not suitable for fast charging on the go, they are very useful for everyday use. Here are a few real-world scenarios where J1772 chargers are most advantageous:
- Home Charging: Many EV owners install Level 2 J1772 chargers at home so they can charge their vehicles overnight and start each day with a fully charged battery. This is very convenient and meets the daily needs of most commuters.
- Public Charging at Malls and Workplaces: Level 2 J1772 chargers are common in public places such as shopping malls, office buildings, and public parking lots. Drivers can “charge” while shopping or working, extending their range without using a DC fast charger.
- Overnight Charging in Hotels: Hotels often provide J1772 connectors for overnight charging, allowing travelers to charge while resting, without having to stop frequently for fast charging during their journey.
The J1772 standard is expected to remain important for years to come, especially for Level 2 charging. As more manufacturers adopt dual standards, such as the J1772 and CCS combo port, EV owners will have greater flexibility to enjoy the convenience of J1772 Level 2 charging while using CCS for DC fast charging when needed.
Conclusion
To sum up, we understand that J1772 is not a fast charger. Designed for Level 1 and Level 2 AC charging, the J1772 standard does not meet the speed standards for fast charging. However, this does not reduce the value of J1772.
Its wide availability, compatibility with almost all electric vehicles, and ease of use make it a reliable choice for daily charging needs.
If you want to buy or wholesale EV charging, please contact the sales staff of the MOREDAYDC website online. We support retail and bulk purchases.
Related reading: CCS1 vs CCS2


