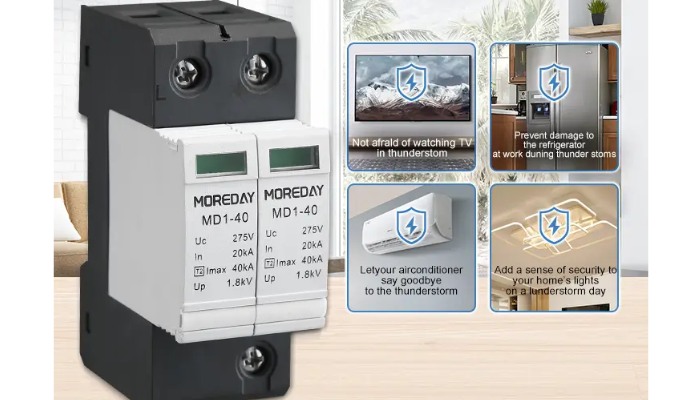
Surge protection devices (SPDs) are the first line of defense against these surges, ensuring the longevity and reliability of electronic equipment.
Properly sizing a surge protector allows for optimal performance and protection. Let’s explore how to size a surge protector and what factors to consider to make the best choice.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhy Size Surge Protection Devices?
Determining the size of a Surge Protective Device (SPD) is a critical step to ensure the safety of the electrical system and the protection of the equipment. Here are some key reasons:
- Protecting Equipment: Different devices have varying tolerance levels to surges. An appropriately sized SPD can effectively protect sensitive equipment, such as computers, communication devices, and industrial control systems, from damage caused by surges.
- Voltage Limitation: SPDs need to operate at specific voltages and limit surge voltage peaks to within the range that equipment can withstand. Excessive surges can cause equipment failure or even fires.
- Current Handling Capacity: The size of the SPD needs to match the potential surge current intensity. An undersized SPD may fail to effectively dissipate surge energy, resulting in protection failure.
- Compliance: Depending on the country and region, electrical standards (such as IEC 61643, IEEE C62.41, etc.) specify requirements for SPD specifications and sizes. Choosing the correct size ensures compliance with these standards and regulations.
- System Configuration: The configuration of the electrical system (such as single-phaseand, and three-phase systems) and the installation location (such as distribution panels, and equipment entry points) also affect SPD selection. A correctly sized SPD ensures effective protection in specific system configurations.
- Service Life: A properly sized SPD can maintain good performance through multiple surge events, extending its service life and avoiding the inconvenience and cost of frequent replacements.
In summary, determining the size of a surge protective device is essential to provide reliable and effective protection in an electrical system, preventing equipment damage and safety risks caused by surges.
What is a Surge Protection Device?
Surge protection devices (SPDs) protect electrical systems from sudden voltage spikes. SPDs protect equipment by diverting excessive voltage away from sensitive components. This action prevents damage and ensures the longevity of electronic equipment.
There are three main types of SPDs, namely Type 1 and Type 2 SPDs and Type 3 SPDs:
- Type 1 SPDs: Installed at the main power service entrance. These devices protect against external surges, such as lightning strikes.
- Type 2 SPDs: Located on the roadside of the service circuit breaker. They protect downstream equipment from internal surges.
- Type 3 SPDs: Placed near specific terminal equipment. They provide targeted protection for individual equipment.
How SPDs Work?
Surge protection devices work by detecting excessive voltage levels. When a surge occurs, the device activates and redirects the surge current to the ground. This action limits the voltage reaching the protected equipment, ensuring safe operation.
SPDs consist of several key components:
- Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs): These absorb and dissipate surge energy. MOVs react quickly to voltage spikes, providing instant protection.
- Gas Discharge Tubes (GDTs): These tubes conduct surge current once a certain voltage threshold is exceeded. GDTs have high surge handling capabilities.
- High Voltage Sensitive Resistors: These resistors react at nanosecond speeds. They control the effects of surges, ensuring smooth operation.
Understanding these components can help select the right SPD for specific needs. Proper selection and installation ensure optimal protection and performance.
Factors to Consider When Selecting SPD Size

There are many aspects to consider when choosing a surge protection device of the right size. Here are some important factors:
1. Determine System Voltage and Configuration
It is important to understand the operating voltage and grounding configuration of the electrical system. Selecting an SPD that matches these voltage levels can ensure effective protection. For example, residential systems generally use lower voltages than industrial systems.
2. Assess Surge Risk
Assessing the frequency and intensity of lightning strikes in the area where the system is located, as well as internal surges (such as motor starting or power switching), can help determine the level of surge risk.
3. Select the Protection Level
Choose the appropriate protection level based on the equipment’s tolerance and protection requirements. Class I is used for high-risk environments, such as direct lightning protection; Class II is used for general power distribution protection; Class III is used for terminal equipment protection.
4. Determine Surge Current Capacity
Correctly match the SPD’s rated current with the system requirements to ensure that the SPD can withstand the maximum surge current in the system to prevent overload and potential damage.
5. Voltage Protection Level (VPR)
Choose an SPD that can limit the surge voltage to an acceptable range for the equipment. The lower the VPR value, the better the protection effect of the equipment.
6. Consider Response Time
Choose an SPD with a short response time to ensure that it can react quickly and limit the voltage when a surge occurs, providing timely protection.
7. Consider Environmental Factors
Consider the working environment of the SPD. Areas prone to lightning strikes or industrial areas with heavy machinery need to choose SPDs that can withstand these conditions to ensure reliable protection.
8. Historical Data
Use historical data to assess the risk level. Reviewing previous surge records in the area can understand the frequency and intensity of surges, thereby guiding the selection of SPDs with appropriate ratings.
9. Product Certification and Standards
Choose SPDs that meet industry standards (such as IEC 61643, UL 1449, etc.) to ensure that their performance and safety meet international and national standards.
10. Compliance Requirements
Ensure that the SPD complies with local regulations and management regulations to avoid legal disputes and ensure optimal protection, which is very important for compliance in different regions.
By understanding electrical system characteristics, assessing surge exposure levels, and complying with standards and regulations, you can ensure that effective surge protection devices are selected.
Moreday’s SPD range offers tailored solutions to meet a variety of protection needs, ensuring the longevity and reliability of electrical systems.
Seek Help from Professionals
Moreday helps users effectively protect electrical systems and equipment from surge damage by providing diversified and high-performance surge protection devices (SPD).
Moreday provides comprehensive technical support and after-sales service to ensure that customers get timely help during the installation and use of SPD and solve any problems that may arise. Welcome to consult us for accurate quotes!


